Channel Mapper#
The purpose of the Channel Mapper is to define the configuration of the QCS’s AWG and digitizer channels relative to the physical qubits. This file will be created during instrument hardware setup and will not need to be changed once the experiment is up and running.
We can write a simple script that generates a Channel Mapper with the above information in the form of a .qcs file. Let us walk through an example of such a script written for a two-qubit system:
import numpy as np
import keysight.qcs as qcs
print(qcs.__version__)
n_qubits = 2
# initialize physical channels
xy_awgs = qcs.Channels(range(n_qubits), "xy_channels", absolute_phase=False)
digs = qcs.Channels(range(n_qubits), "acquire_channels", absolute_phase=True)
readout_awgs = qcs.Channels(
range(n_qubits), "readout_channels", absolute_phase=True
)
2.6.2
The first step is to initialize all virtual channels (control and readout channels) and physical channels (AWG and digitizer channels).
# define physical addresses
xy_awg_address = [qcs.Address(chassis=1, slot=7, channel=1), qcs.Address(1, 7, 2)]
readout_awg_address = qcs.Address(1, 7, 3)
dig_address = qcs.Address(1, 4, 1)
dnc_address = qcs.Address(1, 3, 1)
This includes defining the exact address of each physical channel in the QCS. Note that an address is defined by
three numbers input as arguments to the function qcs.Address() which define the chassis number, slot number,
and channel number.
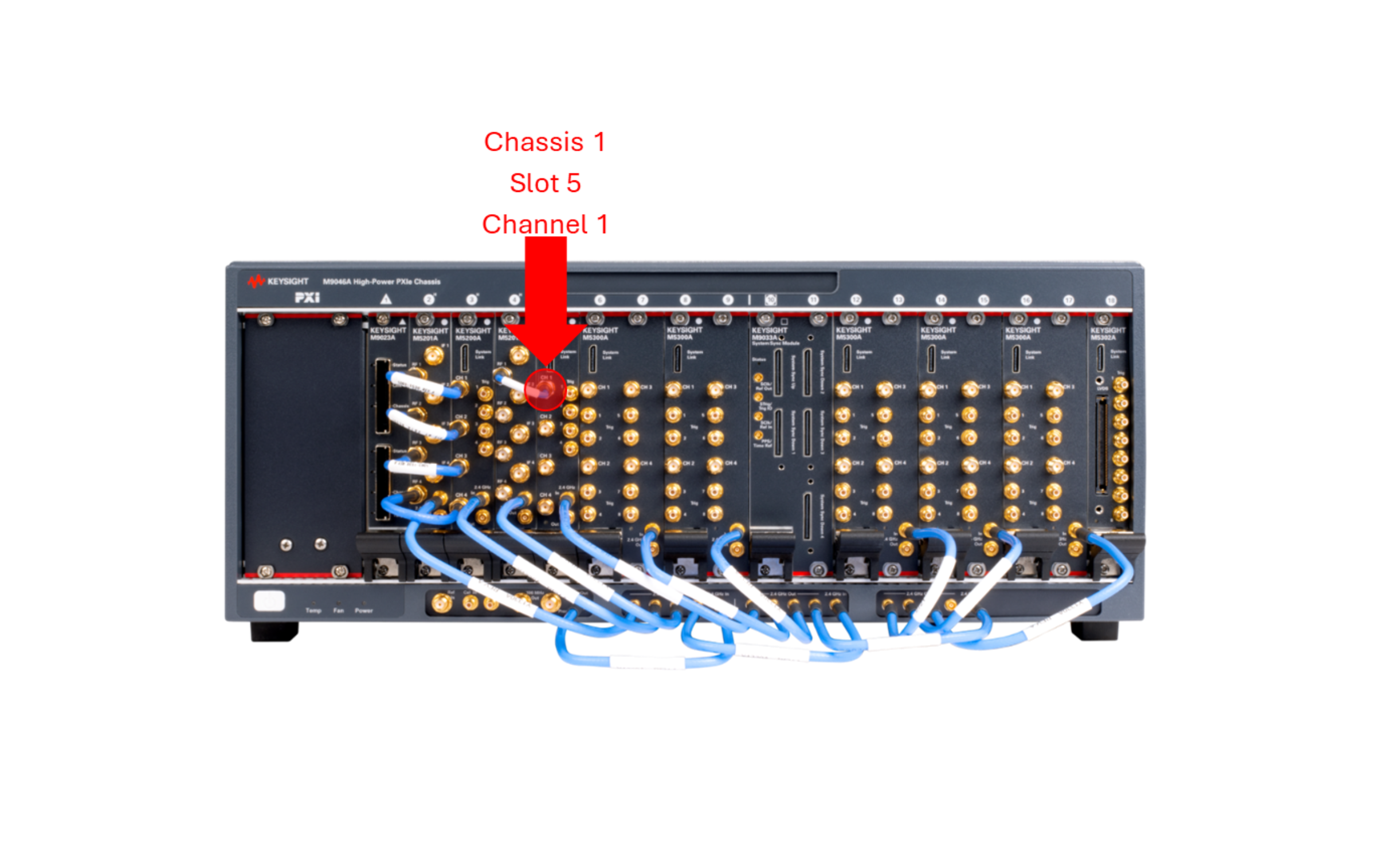
For an example of what the address (1,5,1) looks like in real life, here is a picture:
Next, we should decide which AWG channels will be allotted to XY qubit control - here they are labelled “xy_channels”.
Only one AWG channel will be needed for qubit readout in this system which utilizes multiplexed readout.
# initialize the chan_mapper object
channel_mapper = qcs.ChannelMapper()
# add channel addresses
channel_mapper.add_channel_mapping(
xy_awgs, xy_awg_address, qcs.InstrumentEnum.M5300AWG
)
channel_mapper.add_channel_mapping(
readout_awgs, [readout_awg_address] * n_qubits, qcs.InstrumentEnum.M5300AWG
)
channel_mapper.add_channel_mapping(
digs, [dig_address] * n_qubits, qcs.InstrumentEnum.M5200Digitizer
)
channel_mapper.add_downconverters(dig_address, dnc_address)
# set LO
channel_mapper.set_lo_frequencies([readout_awg_address, dnc_address], 9.8e9)
channel_mapper.set_lo_frequencies(xy_awg_address, 9.8e9)
Finally, we will initialize the channel_mapper object and specify the mappings using these commands.
# generate .qcs file
qcs.save(channel_mapper, "../../assets/chan_mapper.qcs")
The last line of this script will save the channel_mapper object in the form of a .qcs file. This .qcs file will be read
into every experiment executable when using this arrangement of channel mappings. This file does not need to change unless
the physical connections of the experiment are altered.