Download
Download this file as Jupyter notebook: calibration_set.ipynb.
Managing calibration data and linkers
Note
This guide requires the asset
calibration set.
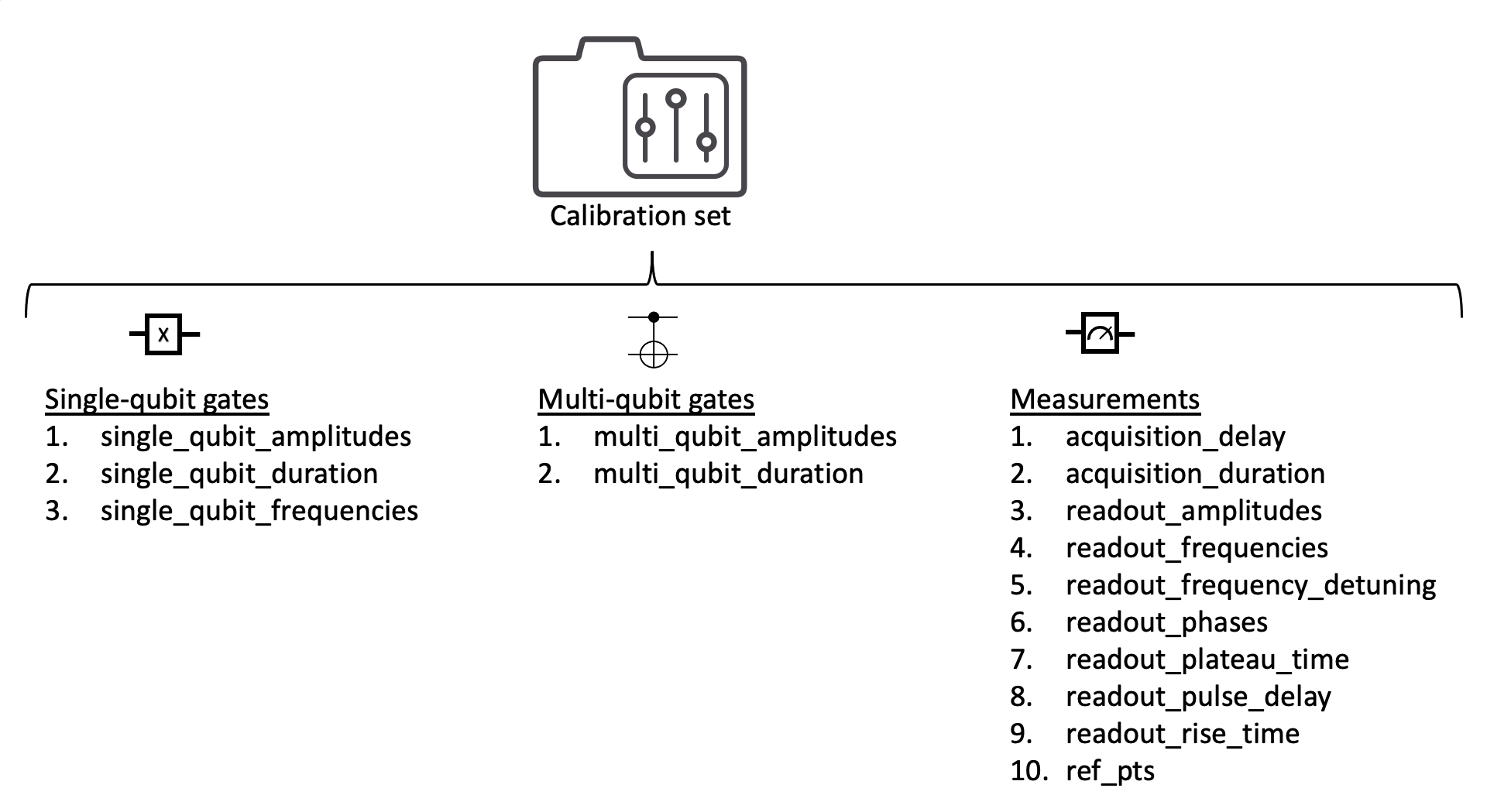
In this guide, we show how to use a CalibrationSet
to manage calibration data and the operation definitions provided by
Linkerss. The
CalibrationSet object provides a way to store and
update calibration data across multiple objects simultaneously. The
CalibrationSet used in this and other guides has
the parameters listed below.
We work with Linkers
for single-qubit \(XY\) rotations and multi-qubit cross-resonance gates, both
common in superconducting systems. See Compiling single-qubit native gates to waveforms,
Compiling multi-qubit native gates to waveforms, and Compiling measurements to waveforms and acquisitions to
learn how to create these objects in detail.
Native gates to compile
We first define the native gates we want to compile, represented by the following
ParametricGates:
[2]:
import keysight.qcs as qcs
import numpy as np
# euler decomposition for XY rotations
layers = [-qcs.PAULIS.sigma_z, qcs.PAULIS.sigma_x, qcs.PAULIS.sigma_z]
zxz = qcs.ParametricGate(layers, ["phi", "theta", "phi"])
# cross-resonance multi-qubit gate
zx_ham = qcs.PAULIS.sigma_z & qcs.PAULIS.sigma_x
cr = qcs.ParametricGate([zx_ham], ["beta"])
Anatomy of a CalibrationSet
A CalibrationSet contains a
VariableSet and a dictionary of
Linkerss. We load one with single-
and multi-qubit linkers for our native gates.
[3]:
calibration_set = qcs.load("../../assets/calibration.qcs")
Variables
The calibration variables can be accessed via
variables.
[4]:
list(calibration_set.variables.variables)
[4]:
[Array(name=single_qubit_frequencies, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=Hz),
Array(name=single_qubit_amplitudes, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=none),
Array(name=multi_qubit_amplitudes, shape=(2,), dtype=float, unit=none),
Scalar(name=single_qubit_duration, value=3e-08, dtype=float, unit=s),
Scalar(name=multi_qubit_duration, value=3e-08, dtype=float, unit=s),
Array(name=readout_frequencies, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=Hz),
Scalar(name=readout_frequency_detuning, value=0.0, dtype=float, unit=Hz),
Array(name=readout_amplitudes, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=none),
Array(name=readout_phases, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=rad),
Scalar(name=readout_plateau_time, value=1e-07, dtype=float, unit=s),
Scalar(name=readout_rise_time, value=3e-08, dtype=float, unit=s),
Scalar(name=readout_pulse_delay, value=4e-08, dtype=float, unit=s),
Scalar(name=acquisition_duration, value=2e-07, dtype=float, unit=s),
Array(name=ref_pts, shape=(4, 2), dtype=complex, unit=none),
Array(name=phis, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=rad),
Array(name=thetas, shape=(4,), dtype=float, unit=none),
Array(name=beta, shape=(2,), dtype=float, unit=none),
Scalar(name=alpha, value=0.33, dtype=float, unit=none)]
While it is convenient to save the full calibration set with variables and linkers
in a single file, it is also possible to save the variables separately using the
export_values() method, which creates
a json file that can easily be edited.
This can be integrated into a workflow where calibration variables can be saved at certain times to track their history.
[5]:
# calibration_set.export_values("calibration_values_Jan_01_2024.qcs")
# the variables stored in this format are sorted by qudit:
print(open("calibration_values_Jan_01_2024.qcs").read())
{
"qudits_0": {
"phis": 0.0,
"thetas": 0.0,
"single_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"single_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5000000000.0,
"readout_pulse_delay": 4E-08,
"readout_rise_time": 3E-08,
"readout_amplitudes": 0.1,
"readout_frequencies": 5800000000.0,
"readout_frequency_detuning": 0.0,
"readout_phases": 0.0,
"readout_plateau_time": 1E-07,
"acquisition_duration": 2E-07,
"ref_pts": {
"real": [
1.0,
1.0
],
"imag": [
1.0,
-1.0
]
}
},
"qudits_1": {
"phis": 0.0,
"thetas": 0.0,
"single_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"single_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5100000000.0,
"readout_pulse_delay": 4E-08,
"readout_rise_time": 3E-08,
"readout_amplitudes": 0.1,
"readout_frequencies": 5850000000.0,
"readout_frequency_detuning": 0.0,
"readout_phases": 0.0,
"readout_plateau_time": 1E-07,
"acquisition_duration": 2E-07,
"ref_pts": {
"real": [
1.0,
1.0
],
"imag": [
1.0,
-1.0
]
}
},
"qudits_2": {
"phis": 0.0,
"thetas": 0.0,
"single_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"single_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5200000000.0,
"readout_pulse_delay": 4E-08,
"readout_rise_time": 3E-08,
"readout_amplitudes": 0.1,
"readout_frequencies": 5900000000.0,
"readout_frequency_detuning": 0.0,
"readout_phases": 0.0,
"readout_plateau_time": 1E-07,
"acquisition_duration": 2E-07,
"ref_pts": {
"real": [
1.0,
1.0
],
"imag": [
1.0,
-1.0
]
}
},
"qudits_3": {
"phis": 0.0,
"thetas": 0.0,
"single_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"single_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5300000000.0,
"readout_pulse_delay": 4E-08,
"readout_rise_time": 3E-08,
"readout_amplitudes": 0.1,
"readout_frequencies": 5950000000.0,
"readout_frequency_detuning": 0.0,
"readout_phases": 0.0,
"readout_plateau_time": 1E-07,
"acquisition_duration": 2E-07,
"ref_pts": {
"real": [
1.0,
1.0
],
"imag": [
1.0,
-1.0
]
}
},
"couplings_0": {
"beta": 0.0,
"multi_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"multi_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5000000000.0,
"alpha": 0.33
},
"couplings_1": {
"beta": 0.0,
"multi_qubit_duration": 3E-08,
"multi_qubit_amplitudes": 0.1,
"single_qubit_frequencies": 5100000000.0,
"alpha": 0.33
}
}
We can edit the exported file and load the edits back in using the
import_values() method:
[6]:
calibration_set.import_values("calibration_values_Jan_01_2024.qcs")
Linkers
The dictionary of linkers can be accessed via
linkers().
[7]:
list(calibration_set.linkers.keys())
[7]:
['single_qubit_linker', 'multi_qubit_linker_suppression', 'measurement_linker']
A CalibrationSet also has an
active_linkers property that can be
used to specify a subset of all available linkers.
By default, all linkers are active and can be set using their names.
[8]:
calibration_set.active_linkers = ["single_qubit_linker", "measurement_linker"]
list(calibration_set.active_linkers.keys())
[8]:
['single_qubit_linker', 'measurement_linker']
Using the Linkers
Now, using the linkers within, we can define gate-level programs and compile them:
[9]:
qubits = qcs.Qudits(range(2))
# define a sample program
program_to_compile = qcs.Program()
# apply X90 on qubit 0 and an X on qubit 1
phis = qcs.Array("phis", value=[0.0, 0.0])
thetas = qcs.Array("thetas", value=[np.pi / 2, np.pi])
program_to_compile.add_parametric_gate(zxz, [phis, thetas], qubits)
# apply (ZX)^1/2 on qubits (0, 1)
beta = qcs.Array("beta", value=[np.pi / 2])
multiqudits = qcs.MultiQudits.from_qudits((qubits[0], qubits[1]))
program_to_compile.add_parametric_gate(cr, [beta], multiqudits)
program_to_compile.draw()
|
Program
Program
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Layer #0
Layer #0
|
Layer #1
Layer #1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
PGATE
ParameterizedGate on ('qudits', 0)
Matrices
|
MULTIGATE
ParameterizedGate on (('qudits', 0), ('qudits', 1))
Matrices
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
PGATE
ParameterizedGate on ('qudits', 1)
Matrices
|
MULTIGATE
ParameterizedGate on (('qudits', 1), ('qudits', 0))
Matrices
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Next, we define a LinkerPass to compile the
program:
[10]:
linker_pass = qcs.LinkerPass(*calibration_set.linkers.values())
program_compiled = linker_pass.apply(program_to_compile)
program_compiled.draw()
|
Program
Program
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Layer #0
Layer #0
|
Layer #1
Layer #1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
RFWaveform on ('xy_channels', 0)
Parameters
|
RFWaveform on ('xy_channels', 0)
Parameters
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
RFWaveform on ('xy_channels', 1)
Parameters
|
RFWaveform on ('xy_channels', 1)
Parameters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
As this program now only contains waveforms, we render it:
[11]:
program_compiled.render(
channel_subplots=False,
lo_frequency=5e9,
sample_rate=qcs.SAMPLE_RATES[qcs.InstrumentEnum.M5300AWG],
)
Updating calibration data
We can update the values of the variables in the
CalibrationSet to update all the variables in
Linkerss that use them. Since the
cross-resonance gate uses the single-qubit frequencies, both waveforms are updated
to reflect the new value.
[12]:
calibration_set.variables.single_qubit_frequencies.value[1] += 100e6
program_compiled.render(
channel_subplots=False,
lo_frequency=5e9,
sample_rate=qcs.SAMPLE_RATES[qcs.InstrumentEnum.M5300AWG],
)
Adding new linkers
Finally, we can create new linkers with the variables in and add new variables to the
calibration set, then use the
add_linker() method to so it can
be saved, loaded, and updated across multiple sessions.
[13]:
operation = calibration_set.linkers["multi_qubit_linker_suppression"].operation
targets = calibration_set.linkers["multi_qubit_linker_suppression"].targets
mq_amp_cals = calibration_set.variables.multi_qubit_amplitudes
frequency_cals = calibration_set.variables.single_qubit_frequencies
# # define a new duration for this gate
mq_dur = qcs.Scalar("multi_qubit_duration_new", value=20e-9, dtype=float)
calibration_set.variables.declare(mq_dur)
gamma = qcs.Array(name="gamma", shape=mq_amp_cals.shape, dtype=float)
prog = qcs.Program()
channels = qcs.Channels([0, 2], "xy_channels")
envelope = qcs.GaussianEnvelope()
pulse = qcs.RFWaveform(mq_dur, envelope, gamma * mq_amp_cals, frequency_cals[1::2])
prog.add_waveform(pulse, channels)
calibration_set.add_linker(
"multi_qubit_linker", qcs.ParameterizedLinker(operation, targets, prog)
)
Download
Download this file as Jupyter notebook: calibration_set.ipynb.
